Major Internet Outages are Getting Bigger and Occurring More Often: A Reflection on the CrowdStrike IT Outage
Author: A.R.E. Taylor (Senior Lecturer in Communications, University of Exeter)
Editor: Aaron Gregory (Editor, 4S Backchannels Global North)
08/12/2024 | Reflections
At 09:30am BST on the 19 July 2024, IT systems around the world had suddenly ground to a halt. Without their computer systems, pharmacies, doctor’s surgeries, airports, train providers, and banks, among other critical services, were unable to operate. Websites and entertainment platforms went offline. Supermarket deliveries were cancelled. Retailer’s payment systems were unable to process transactions. Emergency services were disrupted. TV Channels were unable to air.
Figs. 1-2 Several websites were unable to function due to the outage. Source: Screenshots by A.R.E. Taylor.
The outage highlighted the fragile foundation of global internet infrastructure. The scale and significance of the outage was captured by tech entrepreneur Elon Musk, who took to social media platform X with a simple post that said: ‘biggest IT fail ever’. Others in the IT industry similarly described the event as ‘one of the largest mass outages in IT history’.

Fig. 3 Elon Musk posting about the global IT outage on 19 July 2024. Source: x.com/elonmusk
While it can be hard to quantify the impact of IT outages, this event caused long-lasting and far-reaching disruption across business, industry, and society. Organisations that relied on Windows systems were unable to reboot their computers after a security update was rolled out by the cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike. According to CrowdStrike CEO George Kurtz, a ‘defect’ in one of its software updates for Windows operating systems was identified as the cause of the outage.
The specific piece of technology at fault was the CrowdStrike Falcon Sensor, a cloud-delivered tool used to protect against security breaches, such as malware attacks and hacking threats. The update caused Windows systems to crash, resulting in ‘blue screen of death’ error messages and causing systems to enter a ‘bootloop’ (whereby a computer system continually reboots itself). CrowdStrike software is deeply embedded into the Windows operating system. Microsoft estimated that 8.5 million Windows devices were impacted by the outage, but were keen to place the focus on CrowdStrike by publicly stating, ‘this was not a Microsoft incident’. However, Microsoft Windows’ inability to deal with the issue in a capable manner (other than simply crashing the system) highlighted major deficiencies within the Windows operating system.
In order to resolve the issue, affected organisations had to boot their computers in safe mode, remove the faulty update and then download the safe patched update (in some cases 15 reboots were reportedly needed). This was a time-consuming process, impacting businesses and organisations now facing significant backlogs arising from all of the suspended services. This significant IT outage is estimated to take days, weeks, or even months for fully recovery. The Global Payroll Association also anticipated delays in monthly pay for many workers following the IT outage.
The outage also had a major financial and reputational impact on CrowdStrike. After the event, their shares opened nearly 15% down on the Nasdaq stock exchange in New York, roughly equating to a $12.5 billion decrease in the value of the company. The software firm is expected to pay billions in insurance claims. In the meantime, CrowdStrike reportedly sent some partners a $10 Uber Eats gift card as an apology.
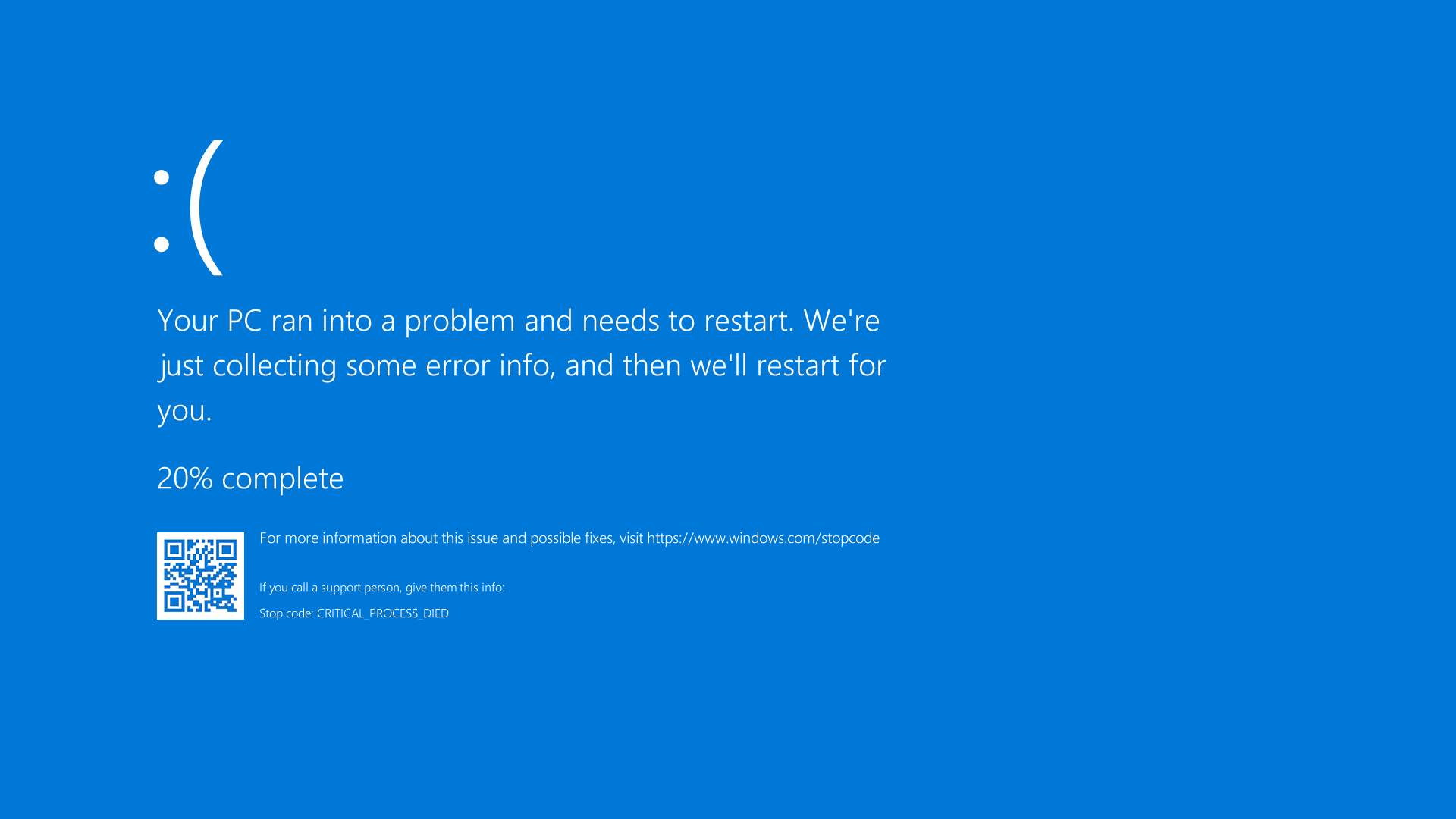
Fig. 4 Blue screen of death error message. Source: Wikimedia Commons.
Who are CrowdStrike?
Until the outage, many of us had never heard of CrowdStrike. Founded in 2011, and based in Austin, Texas, CrowdStrike provides a range of endpoint cybersecurity software solutions to large organisations. Valued at over 80 billion, they first listed their shares publicly on the Nasdaq stock exchange in 2019 and they quickly came to dominate the endpoint security market (their 2023 Q4 earnings report highlights that they have nearly 24,000 customers).
CrowdStrike is not a household name. Unlike other IT security software providers like McAfee, AVG, or Norton, which many people are familiar with because these corporations provide anti-virus software for end-user consumers, CrowdStrike primarily targets enterprise customers. They are one of several small, obscure, yet hugely powerful IT corporations that remain largely unknown to the general public, who are nevertheless responsible for an oversized portion of the globe’s computing infrastructure. Although Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are household names, corporations including Cloudflare, Akamai, Oracle, and Fastly accompany CrowdStrike as lesser-known corporations that form the operational backbone of the internet.
The danger of consolidating computing infrastructure
The CrowdStrike outage provided an eye-opening reminder of the vulnerabilities that arise from the centralisation of computing infrastructure. When one corporation dominates its market to the extent that CrowdStrike does with endpoint security, the result is a single point of failure. The recent outage highlights the risks of IT concentration, alongside the risks that arise from organisational over-dependence on a single operating system provider, with so many organisations relying solely on Windows for their IT provision.
The network model of computing infrastructure originally conceived during the Cold War presents additional concerns. Network computing was initially developed to offer a highly resilient, nuclear attack-proof design comprised by multiple nodes and connections. The idea was that networks would avoid any single point of failure: if one connection should fail, data traffic would continue via the connections that remained. However, as media historians of IT infrastructure have highlighted, this idea was always more of a fantasy than a reality. Far from a massively distributed and decentralised network, the internet quickly came to be dominated by a handful of powerful corporate actors. The rise of cloud computing has further facilitated centralisation, enabling computing resources to be delivered over the internet by a few large companies (Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Digital Reality, Equinix, Oracle). The intensifying consolidation of global computing infrastructure is now leading to a growing number of large-scale IT outages, making the precarious reality of the internet increasingly more apparent. Indeed, the July 2024 event is merely the latest (and potentially the largest yet) of a growing number of outages that have occurred in recent years:
- May 2017 - a power outage brought down a British Airways data centre - which led to the cancellation of over 600 British Airways flights at an estimated cost of £58 million.
- July 2020 - Cloudflare, a global content delivery network (CDN) which more than 10% of all websites rely on, caused a 27-minute outage that led to a 50% collapse in their traffic due to a configuration error.
- June 2021 - some of the world’s most visited websites, including Amazon, PayPal, Reddit, and the New York Times were inaccessible after Fastly, another CDN that provides cloud computing services, suffered a major outage to its service. For those in the IT industry this internet outage highlighted the fragility of the internet’s current architecture and served as ‘a stark reminder that the Internet can fail’.
- July 2021 – a software update from Akamai technologies (whose servers handle over 30% of global web traffic) led to a major outage which impacted services run by UPS, AT&T, Airbnb, and the PlayStation Network.
- October 2021 – Meta, who own Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram, experienced an outage for several hours that affected billions of social media users as well as millions of businesses.
The CrowdStrike outage raises important questions about working conditions at the cybersecurity firm. As an anthropologist who conducts research on data security and fieldwork in the data centre industry, I have spent a lot of time with people who work ‘behind the screens’ of the digital world, delivering the online services we often take for granted. While we still don’t have granular detail about the exact nature of the content update that caused the CrowdStrike crash, it is quite likely that the update was not rigorously checked before it was rolled out. This is not just a technical issue but a socioeconomic issue. In efforts to cut costs and save money, IT companies are often understaffed. This leaves IT staff significantly overworked and under considerable stress in high-pressure jobs where large swathes of society are reliant on the services they deliver, and where expectations for online services to be instantly available at the click of a button are increasingly inflexible. Metaphors like ‘the cloud’ or ‘cyberspace’ present the internet as an ethereal or virtual system devoid of human beings. We forget that the internet relies on a vast array of material infrastructure, carbon-emitting energy, and human labour – it is not an automated process. IT staff often work in highly stressful conditions, beholden to tight deadlines. If a software company is not adequately staffed, or places undue pressure on its staff, corners can be cut, and diagnostic checks might be less thorough. Beyond CrowdStrike, IT staff labouring for thousands of affected organisations worldwide will bear the brunt of outages, working long hours to resolve the issues. The impact of IT failures like this on the mental and physical health of IT staff also remains overlooked.

Fig. 5 A data centre employee conducting a routine diagnostic check. Source: Photo by AR.E. Taylor.
Major IT and internet outages are getting bigger and occurring more often
Sociologists of risk have long argued that the biggest threat to industrialised societies is a dependence on a handful of complex and interdependent infrastructures. The internet now relies on such a complex ecosystem of interdependencies that are ‘black boxes’ to most network professionals. The consolidation of this infrastructure means that power is increasingly concentrated in the hands of a few private companies that dominate their respective markets. This current organisation of internet infrastructure effectively means that more and more eggs are being moved into fewer and fewer baskets, leading to larger outages.
Ironically, in a promotional blog post prior to the outage, CrowdStrike themselves discussed the vulnerability of over-relying on a single major vendor. In the post they note that, ‘If that provider fails, the consequences for its users could be catastrophic.’
Greater societal dependence on the internet means that downtime is more noticeable and more disruptive. This outage may at least prompt organisations to consider diversifying their network security or their operating system providers. We can certainly expect future IT outages – and these may continue to increase in scale and scope - if we don’t address the risk of IT concentration and re-think the business models that underpin the provision of internet infrastructure and online services.
Published: 08/12/2024
